Black Hat SEO is most simply categorized as the application any search engine optimization tactics that the search engines themselves have deemed inappropriate and/or unacceptable.
Google continues to strive for its algorithm to reward websites that bring value to human visitors. Conversely, it seeks to penalize sites that cater instead to the search engine algorithm.
Following this logic, if a technique you’re considering will only increase rankings but add no value to the visitor experience (or worse, further diminish it), it’s a safe guess that your plan would be considered black hat in Google’s eyes.
Below is a list of 30 black hat techniques that you should run like hell from.
At best, they may help your rankings in the short term (though this is far from assured). And at worst, you’ll end up with a penalty and a significant loss in traffic and revenue.
1. Mirror Websites
Hopefully you got the memo in high school (or earlier): plagiarism is bad. Further, it’s not taken lightly by people in positions of authority. Duplicating someone else’s website is highly frowned upon, and when Google finds out (and trust me, they will), they’ll have a nice penalty all lined up just for you.
This technique can also be used for ill in an attempt to create a private blog network. By duplicating your sites, in theory you would be able to grow the relevancy of your sites. That’s the theory anyways. In reality of course, Google has become quite good at ferreting out people that employ this tactic. Avoid it at all costs!
2. Invisible/Hidden Text
Like invisible ink from days of yore, a website owner or designer using this technique would make their text color match the color of their background and proceed to stuff keywords in innocuous places where you visitors wouldn’t be likely to notice or click. The goal may also to be to stuff keywords that wouldn’t otherwise be relevant to the site in order to expand reach and create link juice to pass onto other sites the owner may possess.
Again, at this point, Google has become adept at noticing shysters stooping to this level. Don’t bother with anyone that tells you this is an acceptable or safe practice.
3. Google Bombing
As terrible as this practice is, it’s actually produced some seriously funny results over the years. That of course doesn’t mean you should try this at home, or that it’s at all a practice that can be used to accomplish anything other than a few laughs.
Google bombing is the act of making a search term return unexpected results through the creation of links to the desired website. This is accomplished through creating tons of links to the target website from pages that are optimized for the keyword in question.
4. Link Bait and Switch
This is a crafty one, you can’t help but admire the person who first realized they could do this. It is of course an under-handed and “low” trick to play on someone however, and you should avoid it like the plague (Google penalties continue to be stiff).
The link bait and switch is when you accumulate links to one of your sites while it’s “in disguise.” Once you’ve acquired as many links as you were hoping for, you completely change the website to what you were aiming to perform SEO on the whole time. This is a skeevy way to get high-quality links and often from your competitors.
5. Cloaking
Cloaking is when a website owner codes their site to display one version of a page to search engines and an entirely different one to actual human visitors. We don’t need to go over the nitty gritty of how one goes about accomplishing this. The most important bit is that you don’t get tangled up with this type of SEO behavior.
6. Article Spinning
Automated article spinning is the act of retooling an article just enough to make it evade “duplicate content” detectors. This is clearly a black hat tactic that Google doesn’t like, since it’s essentially allowing you to reuse large chunks of content to earn additional link juice despite the content not bringing any new value to its audience.
Manual article spinning is equally distasteful and perhaps even more illogical than automated spinning. You’re better off writing or commissioning the creation of new original content.
7. Bait and Switch
Ahhhhhh, the bait and switch. The classic, age-old con. Basically, this is where a site owner ranks a site for a set of keywords, and then replaces the site with something completely different once it’s ranking. Any effectiveness this tactic may have once possessed has long since passed. Under Google’s ever vigilant eye, this tactic will (thankfully) have soon completely faded into obscurity.
8. Scraping
Scraping is a broad term for a variety of activities that all fall under the spectrum of things Google frowns upon. Typically the plan goes like this: use a script or program to scrape data from a competitor’s site, and then repurpose it for your own use and profit.
It can also be used to scrape emails for email spam, another lovely tactic that we’ve all surely had experiences with. That Nigerian prince you’re distantly related to? Yeah, that guy was actually a spammer, and he probably scraped your email address from somewhere using ScrapeBox.
9. Link Farms
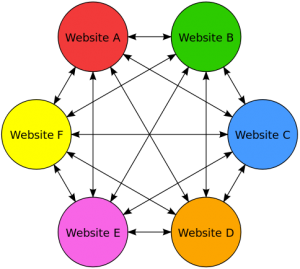
Image credit: Wikipedia
On it’s own this isn’t necessarily a bad thing to do, we all would surely link to our own web pages right? However, if the sole purpose of the sites is to create link juice to feed to one another, the websites cease to have any useful value to visitors and Google will be displeased.
10. Link Exchanging
There’s a recurring theme here you’re probably noticing. It’s frowned upon for you to actively try to accumulate links for the sole purpose of “getting links.” Google wants you to create high-quality content that naturally attracts high-quality links. Exchanged links that are put in place around the same exact time are a pretty clear red-flag that they were swapped, so avoid this practice and save yourself some heartache.
11. Social Network Spamming
Spam in general is considered black hat. So it shouldn’t come as any great surprise then to learn that it’s no different on social media outlets. Sending out an unreasonable number of links across social media, especially if they’re largely irrelevant or don’t serve up any noticeable value to viewers, opens you up to the possibility of a penalty. Did you know that it’s estimated up to 40% of social media accounts are created by spammers? Don’t contribute to that problem, it’s just downright rude!
12. Keyword Stuffing
Back in the day, keyword stuffing was actually an effective technique. The more you jammed keywords into your website, the more Google would find your website to be associated with those search terms you were targeting.
In a post-Panda update world however, keyword density is something that Google carefully monitors. If your content is too focused on keywords, especially if this is so to the point of making your content or site unpleasant to visit and/or use, Google will handily lay the smack-down.
Keywords are still an essential and fundamental part of any SEO you might perform, but be careful not to go overboard, and focus instead upon making your site and content both useful and “human-friendly”.
13. Duplicate Content
Posting duplicate content is the backbone of many of the black hat tactics listed in this article. As such, it deserves special mention for being so super lame. Content should only be used once. It shouldn’t then be re-spun or copied somewhere else.
It doesn’t benefit a visitor to come across the same article on two or three of your sites. It’s just plain frustrating and a selfish (and dangerous) way to try and generate search engine relevancy.
14. Spammy/Unrelated Guest Posting
Guest posting can be a totally legitimate way to earn a link, but unfortunately this practice is sorely abused by a lot of “SEO experts”. Creating lame-duck, tried and true content solely to earn a link, isn’t regarded very highly. This is especially true if the content is unrelated to the author’s site they’re attempting to get a link to.
15. Over-Optimizing (Irrelevant/Unnatural Anchor Text)
Anchor text optimization can still be a useful tool in the right hands, but it’s easy to get carried away. Similar to keyword stuffing, if your anchor text begins to look less and less user-friendly, Google may have a word or two to say about it. You can use this helpful tool to find out if you’re running that risk and how to fix it!
16. Giving out free products for reviews w/ a link
Doing this is just lame. Giving free products for reviews is a pretty standard practice in any industry. But demanding a link is just lame. Don’t do it. Especially since it’s quite possible you’ll get a link anyways. While we’re at it, I’ll throw out a mention that buying reviews is equally distasteful, and while Google may not know it, Amazon just might!
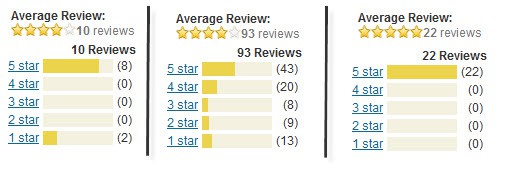
Can you tell which reviews are fake?… -_-
17. Buying placement in low quality directories
This practice is pretty self-explanatory, and you really won’t gain anything from doing it. Bad links aren’t worth much, and you’ll consistently be running the risk of a penalty as they’re often links from a link farm or a PBN. As we mentioned before, Google is on the lookout for those, so just avoid this at all costs!
18. Automated Google Queries
Google is very clear when they state that automated queries are not allowed without prior permission. This includes any kind of automated access attempts and rank checking. If you think Google doesn’t notice this kind of thing, think again! Even the elderly aren’t safe!
19. Doorway Pages
Doorway pages are useless pages that are created solely for the purpose of dominating SERPs for a given set of keywords. Their goal is to siphon traffic to the site-owner’s “money page”. Since these sites offer no value to anyone other than the site-owner however, Google is understandably vehement about them being cause for harsh repercussions.
20. Link Buying
As you may have realized by now, buying links is very clearly considered a black-hat technique. This may seem a little arbitrary given the multitude of ways in which any SEO aficionado can go about obtaining links (with no goal in mind other than accumulating links). Irregardless, buying links is frowned upon, and definitely not recommended.
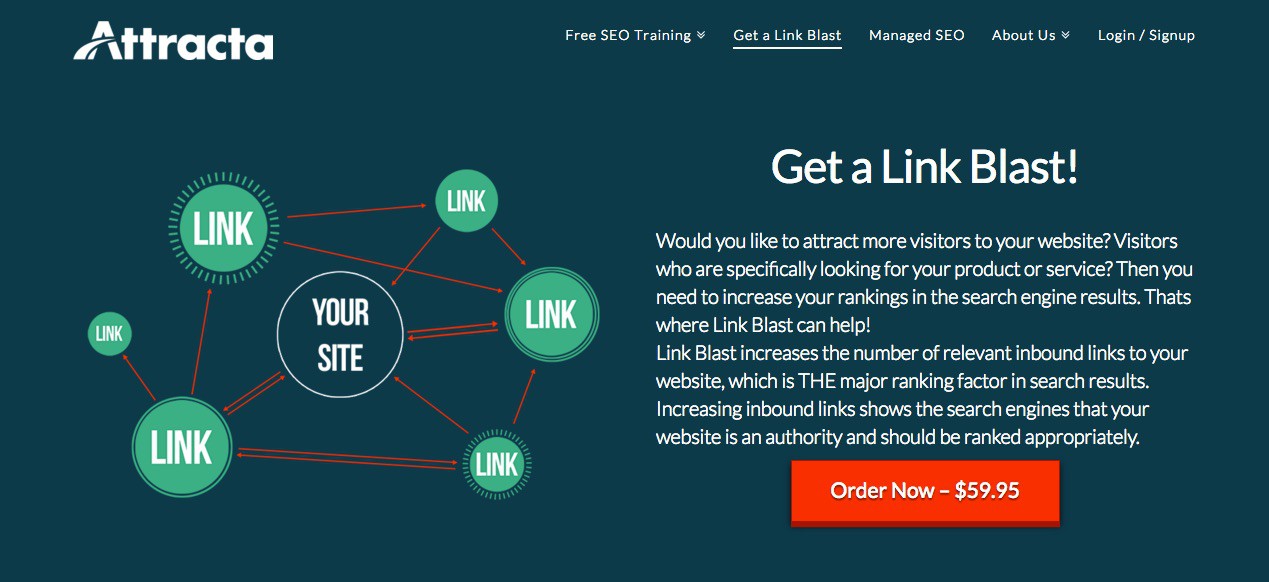
It should also be noted that since respectable web-site owners know that links are not intended to be bought or sold, the links you’ll find available for purchase are often low-quality and could easily be part of a private blog network or link-wheel. Neither of which you want to get involved with!
21. Comment Spamming
Ever been reading a blog and see a bunch of comments that make no sense? Or keyword stuffed comments? Or suspiciously automated-looking comments? Yeah, that’s all comment spam.
The goal is simple, to accumulate as many backlinks and as much traffic as possible by dumping link-filled comments on every blog post in sight. Luckily in today’s internet, this is far less common since recent Google updates.
22. Domain Squatting
Buying and holding onto domains with the purpose of strong-arming a purchase out of a trademark holder is pretty low. What’s worse is it typically involves buying domains that are extremely close to the name of a well-known brand or company, with or without common spelling errors.
It’s perhaps a bit of a stretch to call is SEO, but in a sense it is. Sometimes the squatter will even attempt to monetize the traffic it acquires as a result of its misleading nature.
23. Redirects
Using a 301 is a completely legitimate and standard part of owning and or managing a website. However, as we’ve mentioned before, it’s often hard to have nice things without seeing them spoiled by a few bad apples. Black hat SEO’s will use this technique to trick users into visiting a website they never intended to, which can affect rankings, traffic, and more! As you might expect, this clearly violates Google’s terms of service.
24. Private Blog Networks
A private blog network is a group of sites owned by one individual that are used to create additional SEO value pointed back at the owner’s “money site.” This is often accomplished by buying expired domains that are still indexed and have some residual SEO link-juice. This is a powerful set up for someone to have because they can control every detail including the anchor text and the content on each page. Google has recently cracked down on this practice and a large number of penalties have been handed down for infractions on this front.
25. Footer Link Spam
The footer is often where visitors will go to find additional resources on your site. It’s thus a natural home for a variety of helpful and relevant links. What it should not be used for however, is to jam a bunch of keyword-rich links for the purpose of eeking out just a little bit more SEO value.
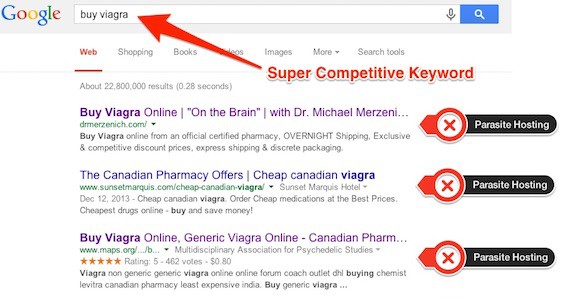
26. Parasite Hosting
Parasite hosting is particularly insidious. This is a situation where a black hat SEO practitioner will create a webpage on a domain they do not own and have it point links at their own money site. This is in an attempt to leech authority and attention from the domain you place the page on and it is accomplished without the site owner’s knowledge or consent.
This will usually come to light eventually however, and it’s such an insulting violation that the penalties are stiff.
27. Page Hijacking
This is when someone creates a site that looks similar (or has a similar snippet) to a popular website but has it redirect traffic to either a malicious or completely unrelated website. It’s lame and won’t work for long. As with the rest of these tactics, not worth the risk!
28. Reporting Competitors
Reporting competitors is a pretty lowly way to go about improving your rankings. Consider it the equivalent of calling the health inspector on a rival restaurant for some imagined flagrant violation of food and safety regulations.
It’s a cheap, short-sighted, and risky way to try and get your SEO kicks. Look elsewhere.
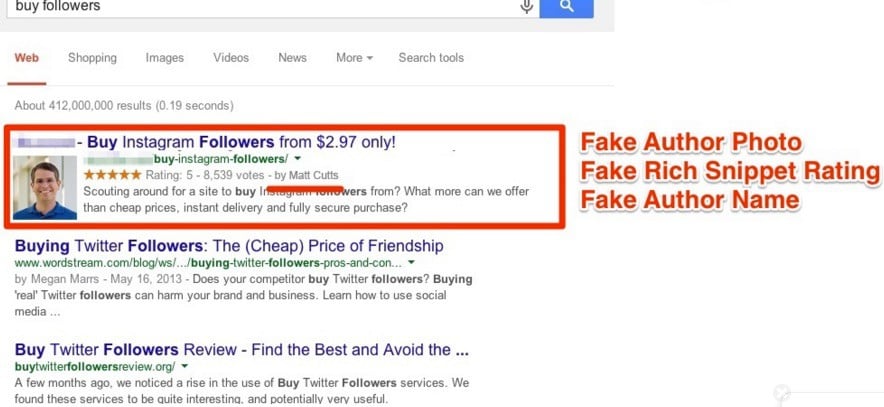
29. Doctoring/Overusing Rich Snippets
Rich snippets are the little tags you see for a given result on a search engine results page. These bad boys are a critical component to a strong funnel. Getting people interested off the get-go is a key method to attract clicks over your competitors.
But, as we’re by now all aware, “too much of a good thing” is a very real concept. Irrelevant phrases and stuffed keywords can make the snippets attract a penalty for spammy structure. Further, falsified reviews and bogus claims are a poor way to go about getting attention.
30. Deceptive Headlines
Last but not least, we have the lovely tactic of using deceptive headlines. This is exactly what it sounds like, titling your article or page one thing, and then having it actually be something completely different. If you’ve ever clicked on an article titled “20 ways to improve your daily life” and ended up on Rick Astley’s “Never Gonna Give You Up” video, you’ve fallen prey to a deceptive headline.